Traumatic brain injuries
Stimulating the plasticity of the brain
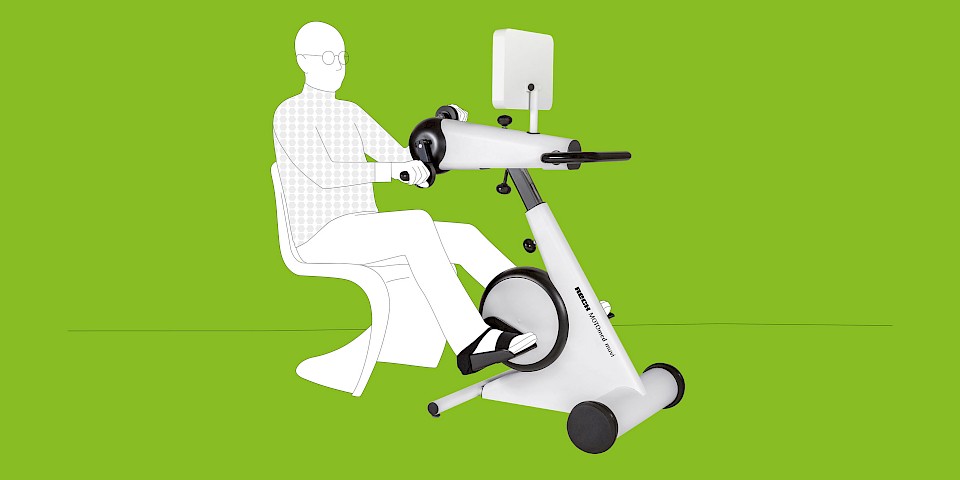
The MOTOmed movement therapy trainer effectively supports occupational- and physiotherapy in patients with traumatic brain injuries. Daily movement activates important body functions, like blood circulation, metabolism, respiration as well as the cardiovascular system, after traumatic brain injury. Moreover, brain activities and self-healing functions are stimulated through regular training. The MOTOmed movement therapy programs enable a specific training and motivate to longer training sessions by motivation games.
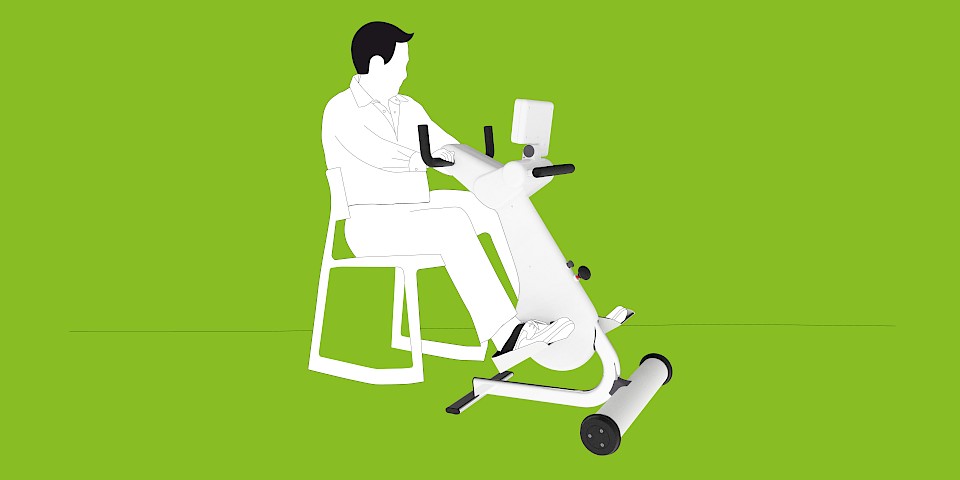
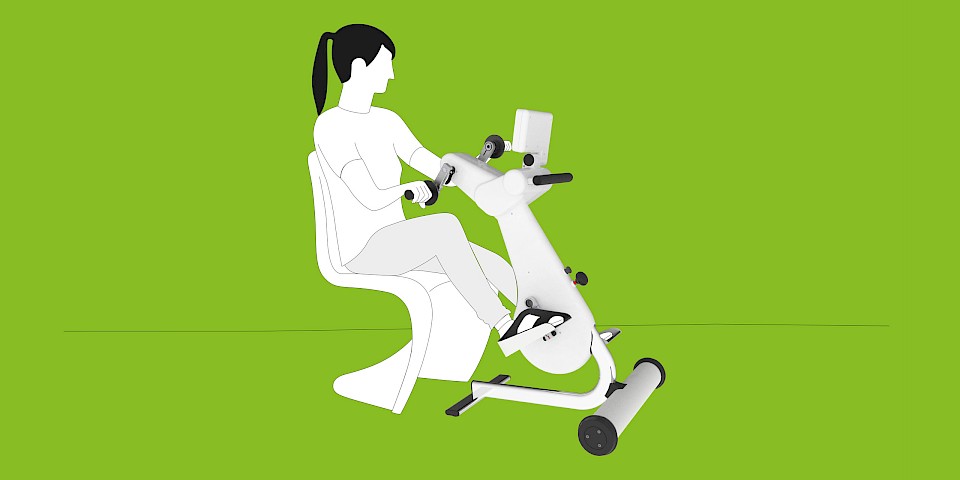
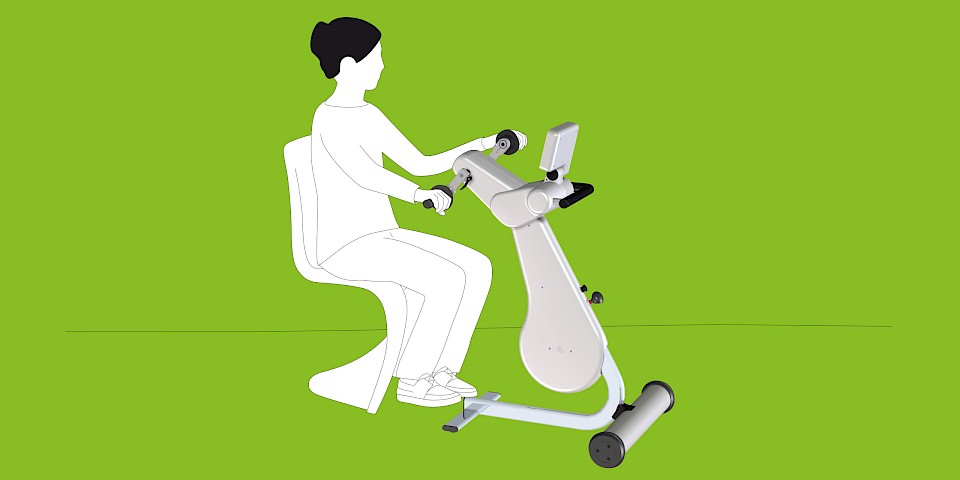
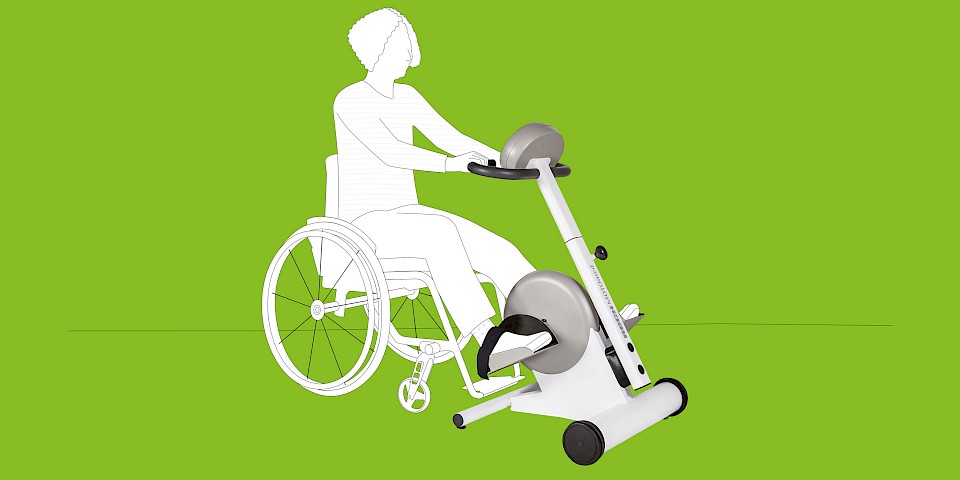
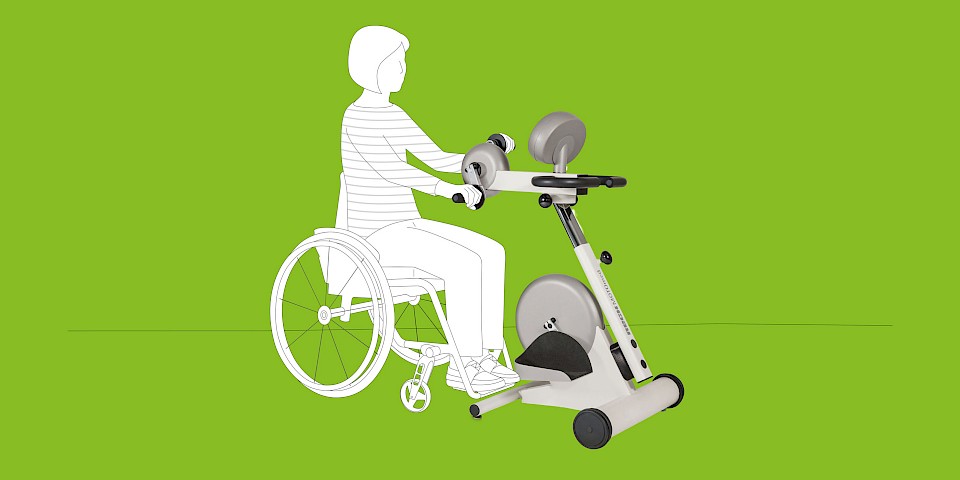
The MOTOmed movement therapy allows patients with traumatic brain injuries a motor-driven, motor-assisted or active movement therapy. The movement can be conducted from the bed, chair or wheelchair. The cyclic movement reduces spasms and loosens and strengthens the muscles in a gentle way.
The device based MOTOmed movement therapy is accepted from government health insurance as a medical aid in Germany. The cost coverage is granted up to 100%.
Configure your personal MOTOmed
Use the MOTOmed Product Configurator to configure your MOTOmed according to your requirements. Quickly, easily and without obligation. Try it out and configure your personal and individualized MOTOmed now.
MOTOmed Movement Therapy
MOTOmed Movement Therapy was developed for people with movement restrictions and complements physical, ergo and sports therapy measures. Users can train while seated in a wheelchair or from a chair. Patients in supine position use MOTOmed from a nursing bed or therapy couch.
In Germany, the device-based movement therapy with the MOTOmed is recognized as an aid for many indications by the statutory health insurance. It is worthwhile to inform yourself!
Therapy modes
passive
The effortless motor driven movement is ideal for the regulation of muscle tone, loosening stiff muscles and for early mobilization after long rests. Passive training stimulates blood circulation, digestion and joint flexibility.
assistive
In motor-supported movement therapy, the function MOTOmed ServoCycling enables easy transition from passive to active training. A motor-supported movement stimulates strength and endurance even with minimal muscle strength.
active
An active training with own muscle power against finely adjustable resistance levels strengthens leg, arm and upper body muscles and stimulates the cardio-vascular system.
Achieving best therapy goals through interval training
Alternating phases of strain and recreation (intervals) through active and passive training give a higher training stimulus which leads to a better therapy success.
Therapeutic goals
- Promote walking
- Reduce the consequences of lack of movement
- Reduce spasticity
- Activate residual muscle strength
- Strengthen the psyche and well-being
- Counteract fatigue