Orthopedics
Improving joint flexibility
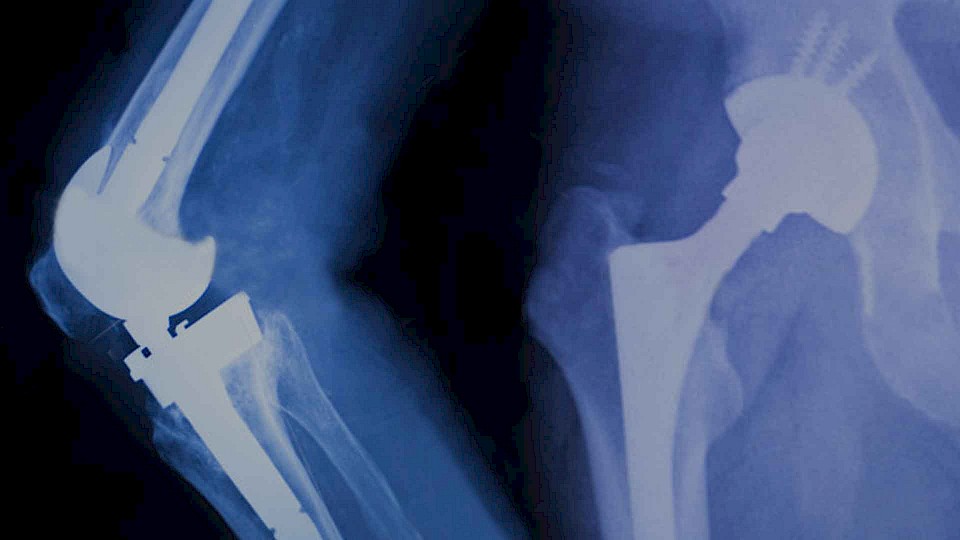
The motor driven movement therapy is a beneficial extension of the therapy spectrum within sports and movement therapy. The motor supported MOTOmed movement completes therapy measures during and after inpatient and ambulatory orthopedic rehabilitation. Especially passive movement and the motor supported active training against finely adjustable resistances enable movement with little load on the joints. Movement control and building up muscles constitute the key targets of MOTOmed Movement Therapy.
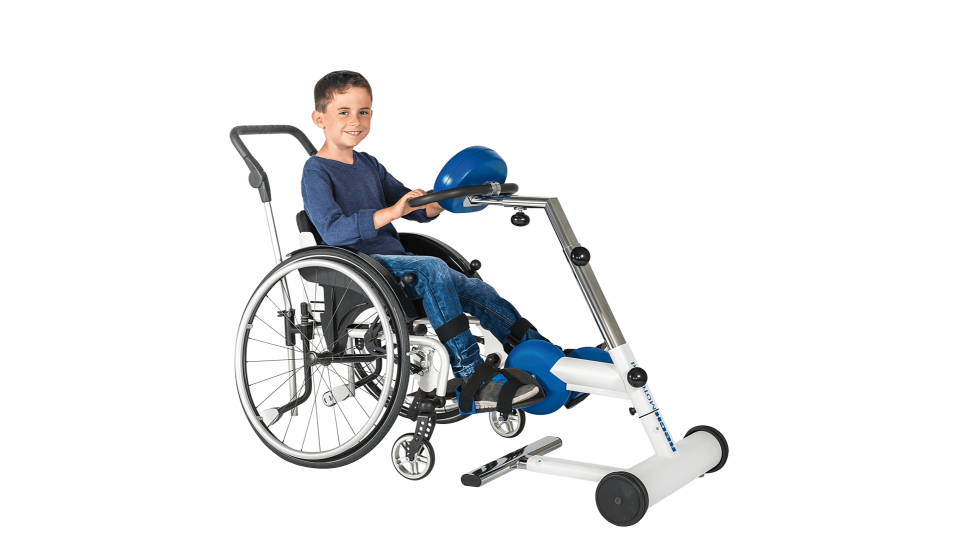
In orthopedic rehabilitation, the MOTOmed movement can improve joint flexibility and strengthens the muscles around the joints, activates blood flow to the joints and relieves the ligaments. Through circular movement with changing pedal radius and a correct sitting position both the extent and range of movement can be adapted individually and increased continuously.
The good usability of the MOTOmed movement therapy devices allows patients to conduct a mostly independent movement training which also constitutes a great benefit for the therapists’ time management.
MOTOmed Movement Therapy
MOTOmed Movement Therapy was developed for people with movement restrictions and complements physical, ergo and sports therapy measures. Users can train while seated in a wheelchair or from a chair. Patients in supine position use MOTOmed from a nursing bed or therapy couch.
In Germany, the device-based movement therapy with the MOTOmed is recognized as an aid for many indications by the statutory health insurance. It is worthwhile to inform yourself!
Therapy modes
passive
The effortless motor driven movement is ideal for the regulation of muscle tone, loosening stiff muscles and for early mobilization after long rests. Passive training stimulates blood circulation, digestion and joint flexibility.
assistive
In motor-supported movement therapy, the function MOTOmed ServoCycling enables easy transition from passive to active training. A motor-supported movement stimulates strength and endurance even with minimal muscle strength.
active
An active training with own muscle power against finely adjustable resistance levels strengthens leg, arm and upper body muscles and stimulates the cardio-vascular system.
Achieving best therapy goals through interval training
Alternating phases of strain and recreation (intervals) through active and passive training give a higher training stimulus which leads to a better therapy success.
Therapeutic goals
- Promote walking
- Reduce the consequences of lack of movement
- Reduce spasticity
- Activate residual muscle strength
- Strengthen the psyche and well-being
- Counteract fatigue
Scientific studies and research results about the MOTOmed movement therapy in the field of orthopedic rehabilitation
Kim H. J., Kwon J. Y., Kim J.S. Kim M. W., Bang H. J., Lee W. I., Ko Y. J. (2006). Preferential Vastus Medialis Oblique Activation Achieved by Isokinetic Cycling at High Angular Velocity. Journal of the Korean Academy of Rehabilitation Medicine, 30(5), 481-484.